Solartracker
This device controls the tracking of solar panels on solar trackers or similar systems based on the sun's position using astronomical data. This tracking is performed on a single axis in the horizontal plane, using elevation and azimuth data of the sun. To prevent shading between the solar panels, a function is implemented that eliminates this shadowing through angle correction. During the day, the tracker moves from east to west. After sunset, the tracker rotates back in the evening. Control is based on geographical coordinates and the time. Depending on the variant, the tracker's angle adjustment is achieved either via its speed (time control without a rotary encoder) or via an absolute rotary encoder. Two limit switches are provided for limiting the rotation and for synchronization. Two relay outputs, one for westward and one for eastward rotation, are implemented for motor control. After a power outage, the tracker control unit immediately moves the solar tracker to the current sun position. It requires only the necessary mains voltage, a reversing protection circuit, and a three-phase motor with a gearbox. One limit switch is installed in each direction, one for eastward and one for westward rotation. They do not need expensive angle sensors for this.
Shadow compensation
When tracking solely by the sun's position, panels can shade each other at low sun angles, depending on panel size and tilt. This significantly reduces the solar system's yield. The electronics prevent this design-related shading by rotating the tracker relative to the direct sunlight in the mornings and evenings. The panels are then illuminated from the side.
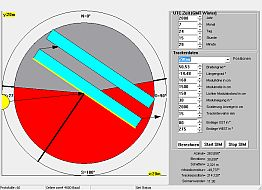
PC simulation and parameterization
The PC program can simulate the sun's path over time at a given geographical location. It can calculate and simulate the shadow cast based on panel size and distance. The simulation data can then be directly used to configure the tracker control system.