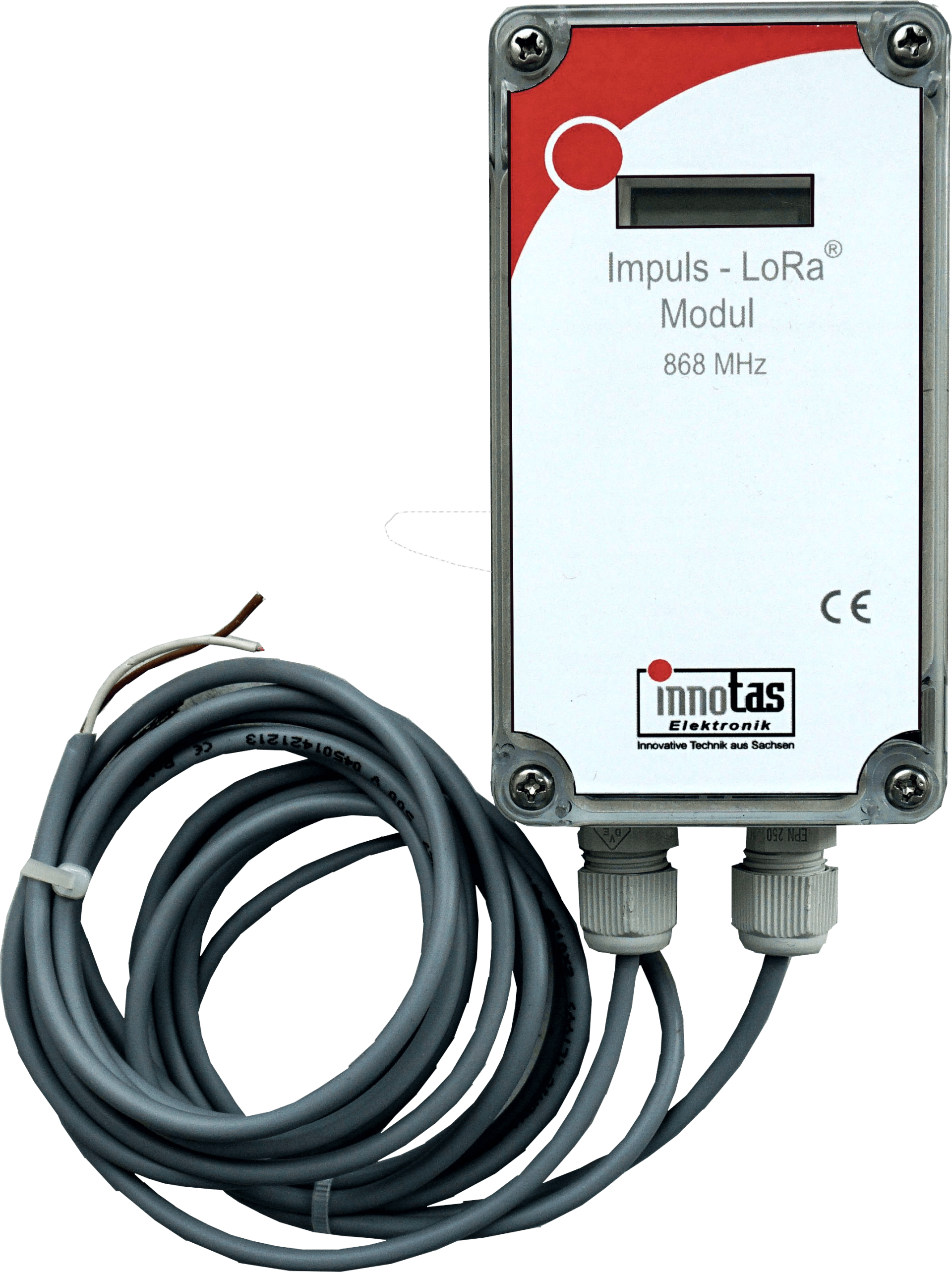
- What is LoRa®?
LoRa® is a long-range wireless technology in which each binary 0 and 1 to be transmitted is transmitted as a frequency pattern (spreading arc). While this increases the protocol length and therefore the transmission time, it can be filtered and received as an extremely weak signal using special techniques. It was developed by the company Semtec. LoRa® is suitable for transmitting small amounts of data per unit of time.
- What is LoRaWAN®?
IBM designed a network protocol specifically for wireless IoT. LoRa® was selected as a suitable transmission method, and thus LoRaWAN® was developed. LoRaWAN® is bidirectional and operates in Class A, B, and C modes. In Class A mode, the LoRa device is asynchronous to the network. In Class B mode, the device maintains synchronization with the network through short synchronization windows. In Class C mode, the device is always wirelessly connected to the network. The energy required for operation increases from Class A to Class C. Mode C is only practical when powered by mains electricity.
- Advantages of LoRaWAN™
The advantage of LoRaWAN® long-range radio technology is that the user is not dependent on an existing receiving network. Users can install and operate one or more LoRaWAN® gateways themselves. A network server is required to operate a private network. Users can set up and operate the server themselves using free software or utilize various network platforms such as TTN, MATCHX, or LORIOT. LoRaWAN® data traffic is bidirectional and uses double encryption (user data and network protocol). LoRaWAN® can only transmit small amounts of data per unit of time. However, the transmission method developed by SEMTECH, in conjunction with the IBM network protocol, enables data transmission over greater distances. The radio protocols themselves range in duration from a few milliseconds to a few seconds. Further information can be found here.
- Using LoRaWAN® in metering
Since LoRa® offers a much greater range and thus significantly larger area coverage per receiver (gateway) in the metering area (wM-BUS) compared to previous radio technologies, lower system costs are necessary. Far fewer receivers (gateways) need to be installed. The operation of expensive, battery-powered wM-BUS gateways is also eliminated, reducing planning and installation costs. Sample calculations show that these costs can be reduced by up to 10%. In a multi-story residential area, instead of installing multiple wM-BUS gateways at each building entrance, only a few LoRa gateways are needed for the entire area.